If you work in the electrical plants or you are interested in the energy sector, you have probably heard about single-line diagrams, especially when it comes to medium-voltage electrical switchgears. But what are they exactly and how are they interpreted? Let’s take a look together.
What is a single-line diagram?
The single-line diagram is a technical design that represents in a simplified and schematic manner the electrical plant of a medium-voltage (MV) switchgear. Its main function is to show the connections between various components, such as switches, measuring transformers, disconnectors, and power lines, using standardized symbols. This type of diagram allows for a quick understanding of the system’s configuration without delving into the wiring details.
How do you read the single-line diagram?
To properly read a single-line diagram, it is necessary to know the electrical symbols and the conventions adopted. Here are some essential steps:
- Identify the main components: symbols that represents circuit-breakers, measuring transformers, disconnectors, fuses, and power lines.
- Follow the power flow: starting from the power source, follow the path through the various devices, to the loads.
- Interpret the connections: the lines represent the conductors and the connections between the components.
- Read the annotations: usually, there are indications of voltage, current, and other electrical parameters.
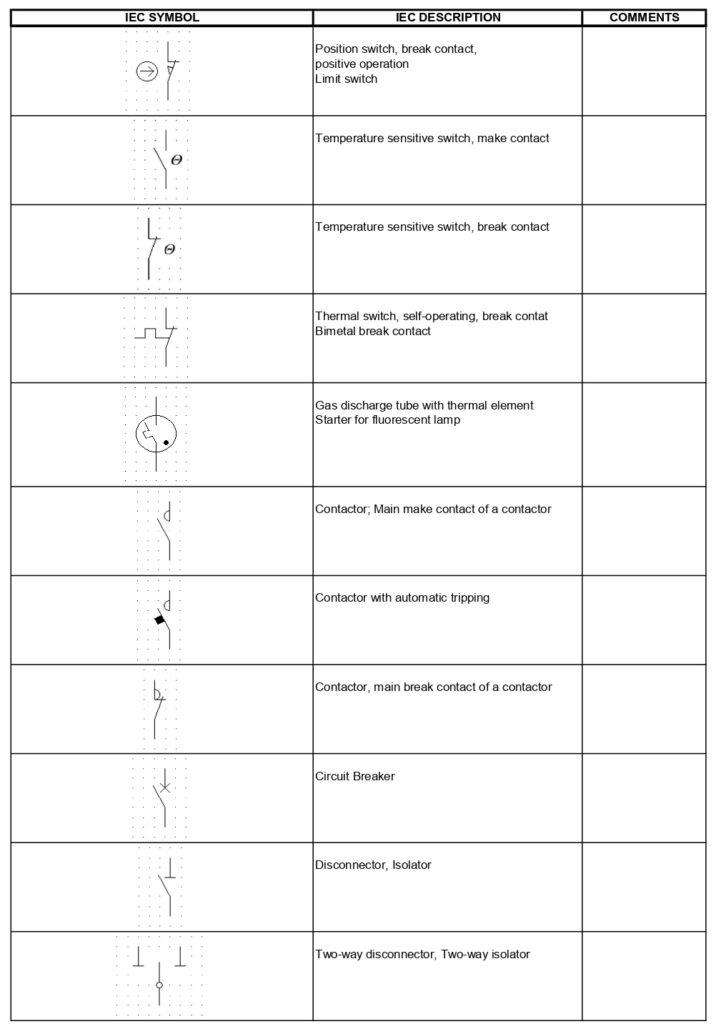
Meaning of the electrical symbolism and international reference standard
The electrical symbolism used in single-line diagrams is regulated by international standards to ensure clarity and uniformity. The main international reference standard is IEC 60617, published by the International Electrotechnical Commission (IEC).
The IEC 60617 standard has the following features:
- Objective: to define standardized graphic symbols to represent electrical components and circuits in single-line and multi-line diagrams.
- Application: used globally, ensuring that diagrams are understandable and consistent across different countries and sectors.
- Content: includes symbols for equipment, protection devices, switches, transformers, power lines, and many other electrical components.
Herewith under we highligth some of the most important and common symbols used in the diagrams.